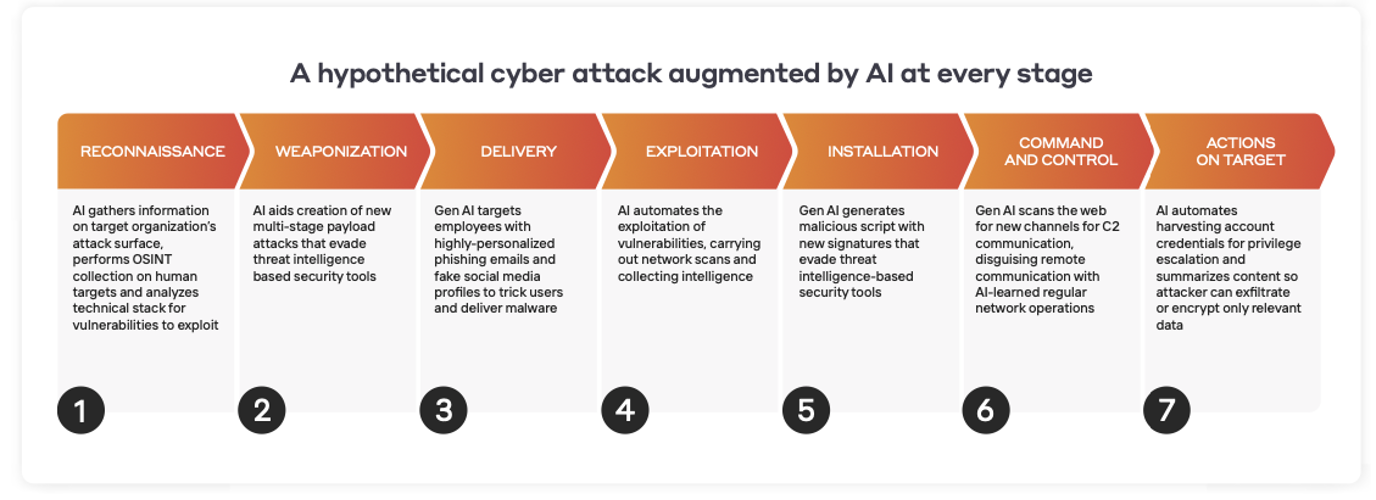
For cyber security experts, it’s hard enough staying on top of the latest threats and emerging attacks without having to deal with a virtual tsunami of alert noise from systems monitoring email, SaaS environments, and endpoints – in addition to IaaS cloud and on-premises networks. Unfortunately, fatigue from these demands can lead to overworking, burnout, and crucially, high employee turnover.
The worldwide industry shortage of 3.5 million cyber security professionals only exacerbates the problem. Not only does it add pressure to the current stock of skilled and available security professionals, but it also raises the stakes for CISOs and other security leaders to find a way to cut through the alert noise while staying on ahead of threat actors who never stop innovating and applying novel malware strains and attack techniques.
Working Smarter Not Harder
One way to help with retention is to empower security teams to break away from monotony and to think creatively and leverage their expertise where it can really add value. Working smarter, rather than harder, is often easier said than done, but by employing automation and AI-driven tools to take on the heavy lifting of threat detection, investigation, and response, human teams can be given the breathing room needed to focus on long-term objectives and think more deeply about their security approaches.
It is important for security programs to continuously level up alongside evolving threat landscapes by questioning existing security operations, and this cannot be achieved during times of hand-to-hand alert combat.
When alerts are fewer, higher quality, and context-heavy, the background to each can be easily explored, whether that’s reevaluating a policy or configuration, or simply asking useful questions around the company’s broader security approach. Work done at this level empowers security teams and fosters growth.
Less is More
Business risk– or the potential impact of cyber disruption– should be the number one concern driving a security team, but lack of resources is a near-constant constraint. Reducing the volume of alerts doesn’t just mean bringing the noise floor up. You can think of the noise floor as an alert threshold: if it is too high then there are fewer alerts, but more threats may be missed, whereas if it is too low, there are high volumes of unhelpful false positives. Freeing up time for the team must not equate to ignoring alerts; it should instead mean focusing on the alerts that matter.
Darktrace’s technologies make this possible, with Darktrace DETECT™ and Cyber AI Analyst working together to address alert fatigue and burnout for security teams while strengthening an organizations’ overall security posture. Cyber AI Analyst essentially takes over the busy work from the human analysts and elevates a team’s overall decision making. Teams now operate at higher levels, as they’re not stuck in mundane alert management and humans are brought in only after the machine and AI have done the heavy lifting.
“Before AI Analyst, we were barely treading water with all of the alerts, most of which were false positives, our old systems produced daily. With AI Analyst, we’ve been able to exponentially reduce those alerts, harden our environment, and get strategic.”
Dr. Robert Spangler, the CISO and Assistant Executive Director of the New Jersey State Bar Association.

Imagine a scenario in which Darktrace observed around 9.6 billion events over a 28-day period. DETECT and Cyber AI Analyst might distill that huge amount of data down into just, say, 54 critical incidents, or just two per day. Here’s how:
9.6 billion events
When trying to understand the full picture, every single puzzle piece counts. That’s why Darktrace’s Self-Learning AI goes wherever your organization has data, integrating with data sources across the digital estate, including network, email, endpoints, OT, cloud, and SaaS environments. And with an open architecture, Darktrace facilitates quick and easy integrations with everything from SIEMs and SOARs to public clouds and the latest Zero Trust technologies. So, any data can become learnable, whether directly ingested or via integration.
By examining this full and contextualized data set, Self-Learning AI builds a constantly evolving understanding of what ‘normal’ looks like for the entire organization. Every connection, every email, app login, resource accessed, VM spun up, PLC reprogrammed, and more become signals from which Darktrace can learn, evaluate, and improve its understanding.
40,404 model breaches
The billions of events are analyzed by Darktrace DETECT, which uses its extensive knowledge of ‘normal’ to draw out hosts of subtle anomalies or ‘AI model breaches.’ Many of these AI model breaches will be weak indicators of threatening activity, and most will not be sufficient to individually signal a threat. For that reason, no human attention is required at this stage. Darktrace DETECT will continue to draw anomalous behaviors from the ongoing stream of events without the need for intervention.
200 incidents
The Cyber AI Analyst takes the total list of model breaches collated by DETECT and performs the truly sophisticated work of determining distinct threat incidents. By piecing together anomalies which may, in themselves, appear harmless, the AI Analyst draws out subtle and often wide-ranging attacks, tracking their route from the initial compromise to the present moment. This creates a much shorter list of genuine threat incidents, but there is still no need for human attention at this stage.
54 critical incidents
Once it has discovered the threat incidents facing an organization, the Cyber AI Analyst begins the crucial processes of triage to determine which incidents need to be surfaced to the security team, and in what order of priority. This supplies the human team with a highly focused briefing of the most pressing threats, massively reducing their overall workload and minimizing or potentially eradicating alert fatigue. In the above example of a month with over 9.6 billion distinct events, the team are left with just two incidents to address per day. These two incidents are clearly presented with natural language-processing and all the most relevant info, including details, devices, and dates.
“When we had other, noisier systems, we didn’t have the time to have truly in-depth discussions or conduct deep investigations, so there were fewer teachable moments for junior team members and fewer opportunities to inform our cybersecurity strategy as a whole,” Spangler said. “Now, we’re not just a better team, we’re more efficient, responsive, and informed than we’ve ever been. We’re all better cyber security professionals as a result.”
In the event of a breach, CISOs and security leaders want the full incident report, and they want it yesterday. The promise of AI is to handle specific tasks at a speed and scale that humans can’t. Going from 9.6 billion events to 54 incidents demonstrates the scale, but it’s important to consider the impact of speed here as well, as the Cyber AI Analyst works in real time, meaning all relevant events are presented in an easy to consume downloadable report available immediately upon investigation.
This isn’t a black box either; every step of the AI Analyst’s investigation process is visible to the human team. Not only can they see the relevant events and breaches that led to the incident, but if required, they can pivot into them easily with a click. If the investigation requires going all the way down to the metadata level to easily peruse the filtered events of the 9.6 billion overall signals or even to PCAP data, those are available and easy to find too.
Since DETECT and Cyber AI Analyst not only reduce alert fatigue but also simplify incident investigations, security teams feel empowered and experience less burnout.
“We’ve been stable and have had minimal turnover since we started using AI Analyst,” Spangler said. “We’re not scrambling to keep up with noisy and time-consuming false positives, making the investigations that we undertake stimulating and– I say this cautiously– fun! Put simply, the thing we all love about this career, the virtual chess game we play with attackers, is a lot more fun when you know you’re going to win.”
Respuesta autónoma
Organizations that deploy Darktrace RESPOND™ can address the incidents raised by DETECT and the Cyber AI Analyst autonomously, and in mere seconds. Using the full context of the organization built up by Self-Learning AI, RESPOND takes the least disruptive measures necessary to disarm threats at machine speed. By the time the security team learns about the attack, it is already contained, continuing to save them from the hand-to-hand combat of threat fighting.
With day-to-day threat detection, response, and analysis taken care of, security teams are free to give full and sustained attention to their overall security posture. Neutralized threats may yet reveal broader security gaps and potential improvements which the team now has the time and headspace to pursue.
For example, discovering a trend that users are uploading potentially sensitive data via third-party file-sharing services might lead to a discussion about whether it should be company policy to block access to this service, reducing to zero the number of future alerts that would have been triggered by this behavior. Importantly, this wouldn’t be altering the aforementioned noise floor, but instead fundamentally altering security policies to align with the needs of the business, which could indirectly affect future alerting, as activities may subside.
As a result, practitioners find more value in their work, security teams efforts are optimized, and organizations are strengthened overall.
“We’re now focused on the items that AI Analyst alerts us to, which are always worth looking into because they either identify an activity that we need to get eyes on and/or provide us with insight into ways we can harden our network,” Spangler said. “The hardening that we’ve done has been incalculably beneficial– it’s one of the reasons we get fewer alerts, and it’s also protected us against a wide variety of threats.”


























.png)