When security teams discuss the possibility of phishing attacks targeting their organization, often the first reaction is to assume it is inevitable because of the users. Users are typically referenced in cyber security conversations as organizations’ greatest weaknesses, cited as the causes of many grave cyber-attacks because they click links, open attachments, or allow multi-factor authentication bypass without verifying the purpose.
While for many, the weakness of the user may feel like a fact rather than a theory, there is significant evidence to suggest that users are psychologically incapable of protecting themselves from exploitation by phishing attacks, with or without regular cyber awareness trainings. The psychology of trust and the nature of human reliance on technology make the preparation of users for the exploitation of that trust in technology very difficult – if not impossible.
This Darktrace long read will highlight principles of psychological and sociological research regarding the nature of trust, elements of the trust that relate to technology, and how the human brain is wired to rely on implicit trust. These principles all point to the outcome that humans cannot be relied upon to identify phishing. Email security driven by machine augmentation, such as AI anomaly detection, is the clearest solution to tackle that challenge.
What is the psychology of trust?
Psychological and sociological theories on trust largely centre around the importance of dependence and a two-party system: the trustor and the trustee. Most research has studied the impacts of trust decisions on interpersonal relationships, and the characteristics which make those relationships more or less likely to succeed. In behavioural terms, the elements most frequently referenced in trust decisions are emotional characteristics such as benevolence, integrity, competence, and predictability.1
Most of the behavioural evaluations of trust decisions survey why someone chooses to trust another person, how they made that decision, and how quickly they arrived at their choice. However, these micro-choices about trust require the context that trust is essential to human survival. Trust decisions are rooted in many of the same survival instincts which require the brain to categorize information and determine possible dangers. More broadly, successful trust relationships are essential in maintaining the fabric of human society, critical to every element of human life.
Trust can be compared to dark matter (Rotenberg, 2018), which is the extensive but often difficult to observe material that binds planets and earthly matter. In the same way, trust is an integral but often a silent component of human life, connecting people and enabling social functioning.2
Defining implicit and routine trust
As briefly mentioned earlier, dependence is an essential element of the trusting relationship. Being able to build a routine of trust, based on the maintenance rather than establishment of trust, becomes implicit within everyday life. For example, speaking to a friend about personal issues and life developments is often a subconscious reaction to the events occurring, rather than an explicit choice to trust said friend each time one has new experiences.
Active and passive levels of cognition are important to recognize in decision-making, such as trust choices. Decision-making is often an active cognitive process requiring a lot of resource from the brain. However, many decisions occur passively, especially if they are not new choices e.g. habits or routines. The brain’s focus turns to immediate tasks while relegating habitual choices to subconscious thought processes, passive cognition. Passive cognition leaves the brain open to impacts from inattentional blindness, wherein the individual may be abstractly aware of the choice but it is not the focus of their thought processes or actively acknowledged as a decision. These levels of cognition are mostly referenced as “attention” within the brain’s cognition and processing.3
This idea is essentially a concept of implicit trust, meaning trust which is occurring as background thought processes rather than active decision-making. This implicit trust extends to multiple areas of human life, including interpersonal relationships, but also habitual choice and lifestyle. When combined with the dependence on people and services, this implicit trust creates a haze of cognition where trust is implied and assumed, rather than actively chosen across a myriad of scenarios.
Trust and technology
As researchers at the University of Cambridge highlight in their research into trust and technology, ‘In a fundamental sense, all technology depends on trust.’ The same implicit trust systems which allow us to navigate social interactions by subconsciously choosing to trust, are also true of interactions with technology. The implied trust in technology and services is perhaps most easily explained by a metaphor.
Most people have a favourite brand of soda. People will routinely purchase that soda and drink it without testing it for chemicals or bacteria and without reading reviews to ensure the companies that produce it have not changed their quality standards. This is a helpful, representative example of routine trust, wherein the trust choice is implicit through habitual action and does not mean the person is actively thinking about the ramifications of continuing to use a product and trust it.
The principle of dependence is especially important in trust and technology discussions, because the modern human is entirely reliant on technology and so has no way to avoid trusting it.5 Specifically important in workplace scenarios, employees are given a mandatory set of technologies, from programs to devices and services, which they must interact with on a daily basis. Over time, the same implicit trust that would form between two people forms between the user and the technology. The key difference between interpersonal trust and technological trust is that deception is often much more difficult to identify.
The implicit trust in workplace technology
To provide a bit of workplace-specific context, organizations rely on technology providers for the operation (and often the security) of their devices. The organizations also rely on the employees (users) to use those technologies within the accepted policies and operational guidelines. The employees rely on the organization to determine which products and services are safe or unsafe.
Within this context, implicit trust is occurring at every layer of the organization and its technological holdings, but often the trust choice is only made annually by a small security team rather than continually evaluated. Systems and programs remain in place for years and are used because “that’s the way it’s always been done. Within that context, the exploitation of that trust by threat actors impersonating or compromising those technologies or services is extremely difficult to identify as a human.
For example, many organizations utilize email communications to promote software updates for employees. Typically, it would consist of email prompting employees to update versions from the vendors directly or from public marketplaces, such as App Store on Mac or Microsoft Store for Windows. If that kind of email were to be impersonated, spoofing an update and including a malicious link or attachment, there would be no reason for the employee to question that email, given the explicit trust enforced through habitual use of that service and program.
Inattentional blindness: How the brain ignores change
Users are psychologically predisposed to trust routinely used technologies and services, with most of those trust choices continuing subconsciously. Changes to these technologies would often be subject to inattentional blindness, a psychological phenomenon wherein the brain either overwrites sensory information with what the brain expects to see rather than what is actually perceived.
A great example of inattentional blindness6 is the following experiment, which asks individuals to count the number of times a ball is passed between multiple people. While that is occurring, something else is going on in the background, which, statistically, those tested will not see. The shocking part of this experiment comes after, when the researcher reveals that the event occurring in the background not seen by participants was a person in a gorilla suit moving back and forth between the group. This highlights how significant details can be overlooked by the brain and “overwritten” with other sensory information. When applied to technology, inattentional blindness and implicit trust makes spotting changes in behaviour, or indicators that a trusted technology or service has been compromised, nearly impossible for most humans to detect.
With all this in mind, how can you prepare users to correctly anticipate or identify a violation of that trust when their brains subconsciously make trust decisions and unintentionally ignore cues to suggest a change in behaviour? The short answer is, it’s difficult, if not impossible.
How threats exploit our implicit trust in technology
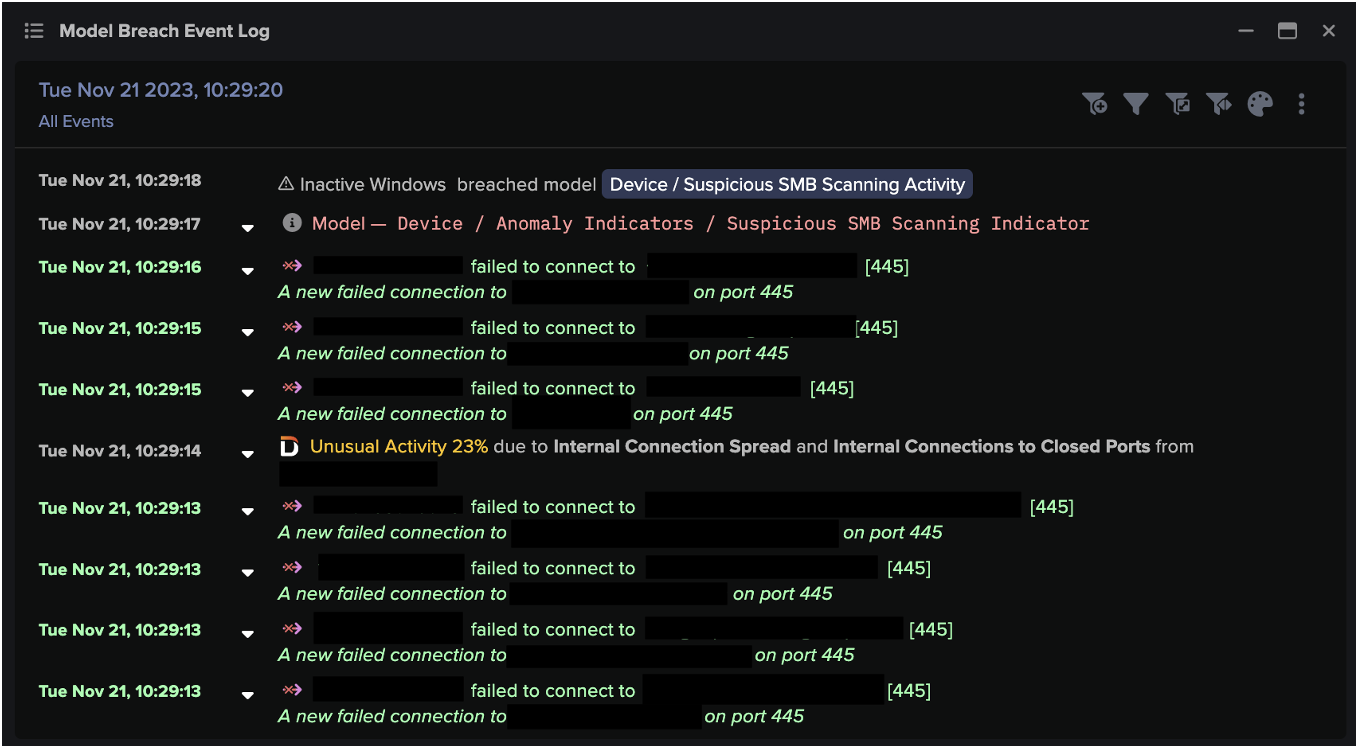
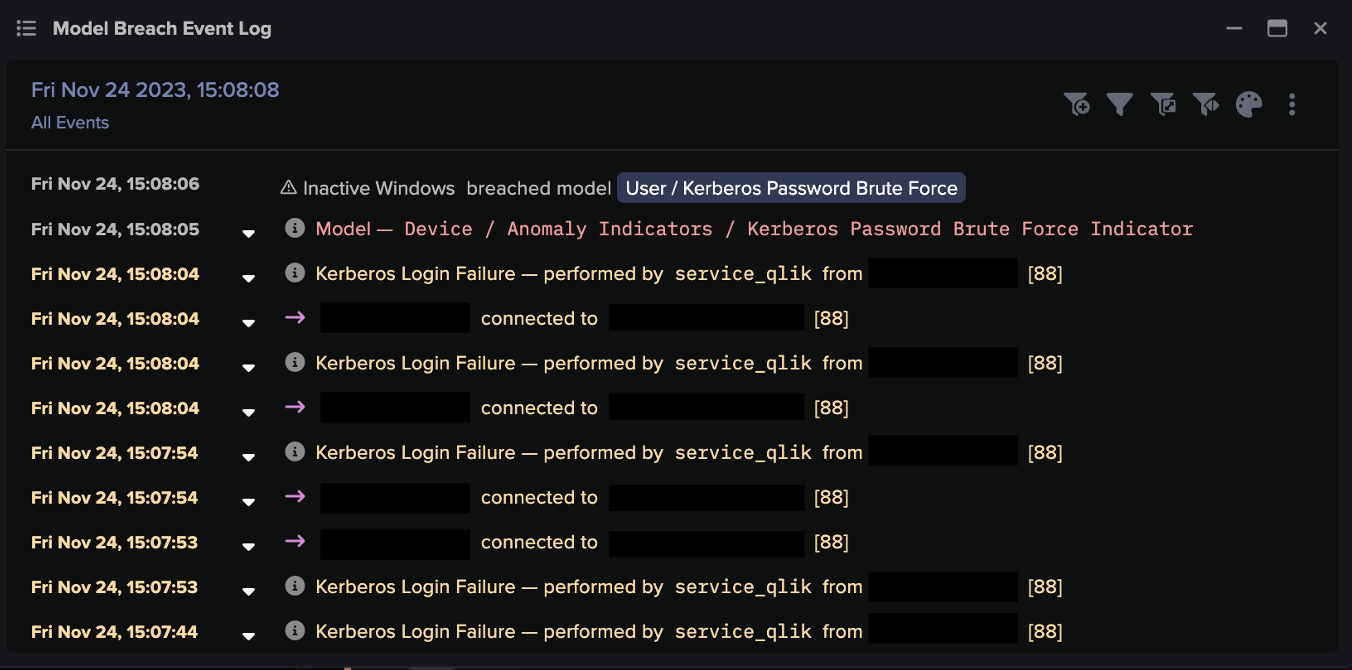
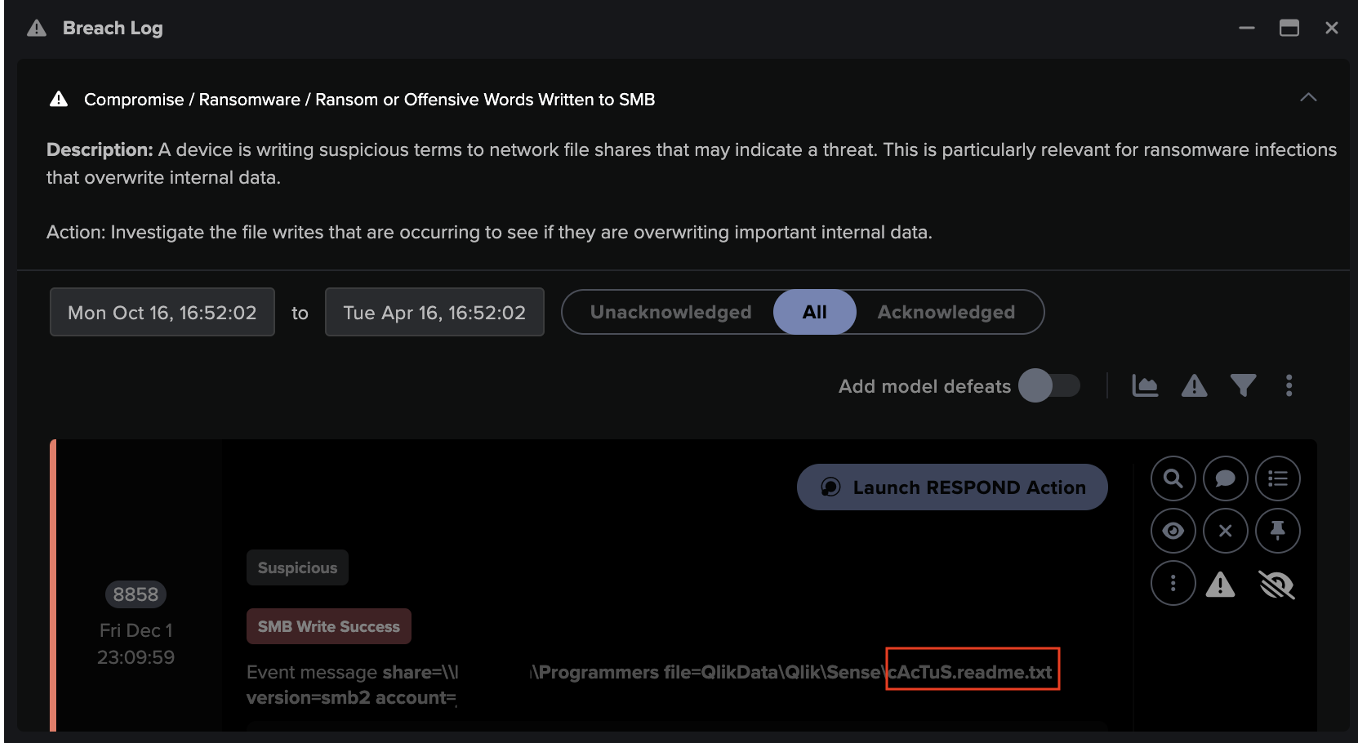
Most cyber threats are built around the idea of exploiting the implicit trust humans place in technology. Whether it’s techniques like “living off the land”, wherein programs normally associated with expected activities are leveraged to execute an attack, or through more overt psychological manipulation like phishing campaigns or scams, many cyber threats are predicated on the exploitation of human trust, rather than simply avoiding technological safeguards and building backdoors into programs.
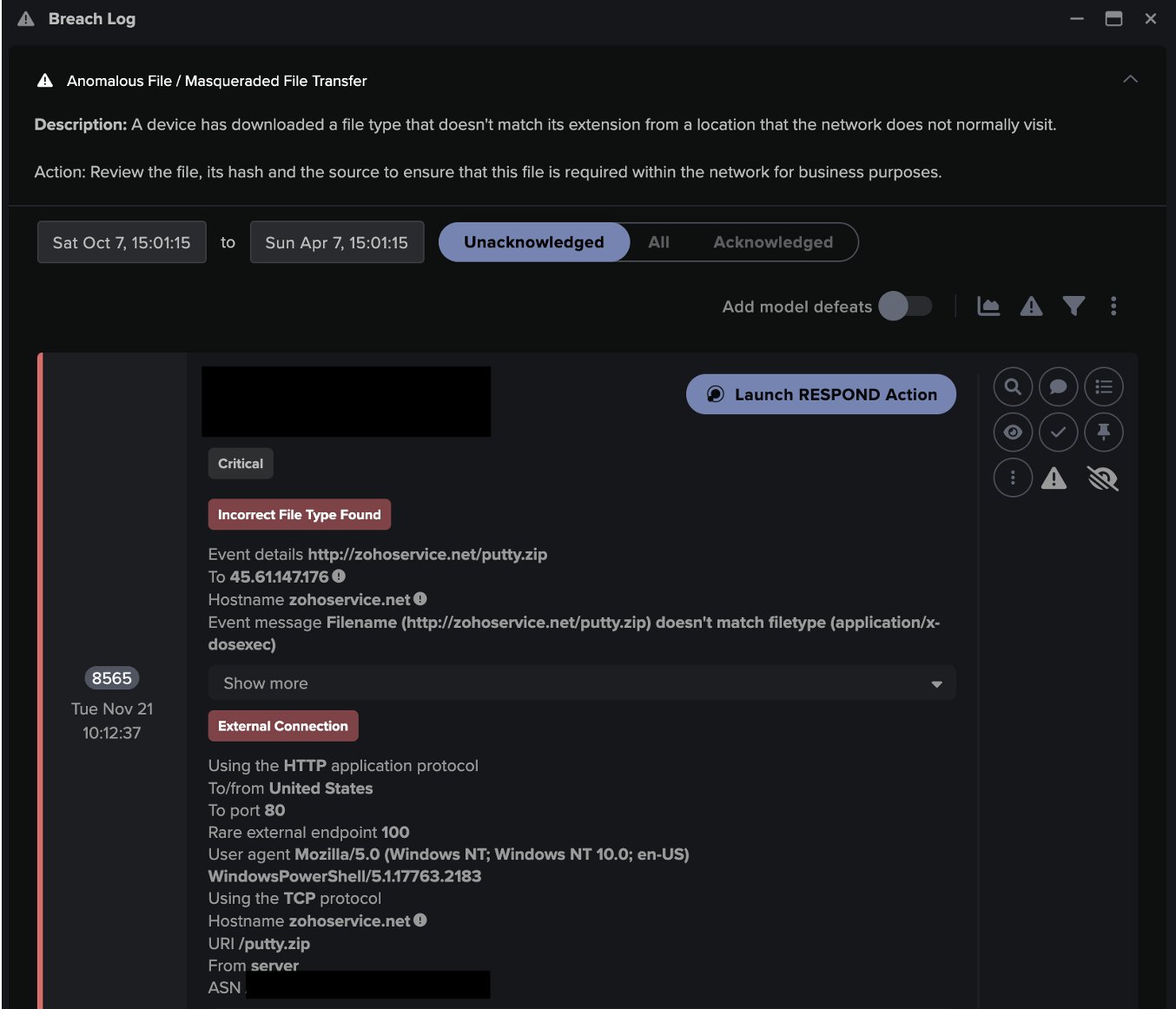
In the case of phishing, it is easy to identify the attempts to leverage the trust of users in technology and services. The most common example of this would be spoofing, which is one of the most common tactics observed by Darktrace/Email. Spoofing is mimicking a trusted user or service, and can be accomplished through a variety of mechanisms, be it the creation of a fake domain meant to mirror a trusted link type, or the creation of an email account which appears to be a Human Resources, Internal Technology or Security service.
In the case of a falsified internal service, often dubbed a “Fake Support Spoof”, the user is exploited by following instructions from an accepted organizational authority figure and service provider, whose actions should normally be adhered to. These cases are often difficult to spot when studying the sender’s address or text of the email alone, but are made even more difficult to detect if an account from one of those services is compromised and the sender’s address is legitimate and expected for correspondence. Especially given the context of implicit trust, detecting deception in these cases would be extremely difficult.
How email security solutions can solve the problem of implicit trust
How can an organization prepare for this exploitation? How can it mitigate threats which are designed to exploit implicit trust? The answer is by using email security solutions that leverage behavioural analysis via anomaly detection, rather than traditional email gateways.
Expecting humans to identify the exploitation of their own trust is a high-risk low-reward endeavour, especially when it takes different forms, affects different users or portions of the organization differently, and doesn’t always have obvious red flags to identify it as suspicious. Cue email security using anomaly detection as the key answer to this evolving problem.
Anomaly detection enabled by machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) removes the inattentional blindness that plagues human users and security teams and enables the identification of departures from the norm, even those designed to mimic expected activity. Using anomaly detection mitigates multiple human cognitive biases which might prevent teams from identifying evolving threats, and also guarantees that all malicious behaviour will be detected. Of course, anomaly detection means that security teams may be alerted to benign anomalous activity, but still guarantees that no threat, no matter how novel or cleverly packaged, won’t be identified and raised to the human security team.
Utilizing machine learning, especially unsupervised machine learning, mimics the benefits of human decision making and enables the identification of patterns and categorization of information without the framing and biases which allow trust to be leveraged and exploited.
For example, say a cleverly written email is sent from an address which appears to be a Microsoft affiliate, suggesting to the user that they need to patch their software due to the discovery of a new vulnerability. The sender’s address appears legitimate and there are news stories circulating on major media providers that a new Microsoft vulnerability is causing organizations a lot of problems. The link, if clicked, forwards the user to a login page to verify their Microsoft credentials before downloading the new version of the software. After logging in, the program is available for download, and only requires a few minutes to install. Whether this email was created by a service like ChatGPT (generative AI) or written by a person, if acted upon it would give the threat actor(s) access to the user’s credential and password as well as activate malware on the device and possibly broader network if the software is downloaded.
If we are relying on users to identify this as unusual, there are a lot of evidence points that enforce their implicit trust in Microsoft services that make them want to comply with the email rather than question it. Comparatively, anomaly detection-driven email security would flag the unusualness of the source, as it would likely not be coming from a Microsoft-owned IP address and the sender would be unusual for the organization, which does not normally receive mail from the sender. The language might indicate solicitation, an attempt to entice the user to act, and the link could be flagged as it contains a hidden redirect or tailored information which the user cannot see, whether it is hidden beneath text like “Click Here” or due to link shortening. All of this information is present and discoverable in the phishing email, but often invisible to human users due to the trust decisions made months or even years ago for known products and services.
AI-driven Email Security: The Way Forward
Email security solutions employing anomaly detection are critical weapons for security teams in the fight to stay ahead of evolving threats and varied kill chains, which are growing more complex year on year. The intertwining nature of technology, coupled with massive social reliance on technology, guarantees that implicit trust will be exploited more and more, giving threat actors a variety of avenues to penetrate an organization. The changing nature of phishing and social engineering made possible by generative AI is just a drop in the ocean of the possible threats organizations face, and most will involve a trusted product or service being leveraged as an access point or attack vector. Anomaly detection and AI-driven email security are the most practical solution for security teams aiming to prevent, detect, and mitigate user and technology targeting using the exploitation of trust.
References
1https://www.kellogg.northwestern.edu/trust-project/videos/waytz-ep-1.aspx
2Rotenberg, K.J. (2018). The Psychology of Trust. Routledge.
3https://www.cognifit.com/gb/attention
4https://www.trusttech.cam.ac.uk/perspectives/technology-humanity-society-democracy/what-trust-technology-conceptual-bases-common
5Tyler, T.R. and Kramer, R.M. (2001). Trust in organizations : frontiers of theory and research. Thousand Oaks U.A.: Sage Publ, pp.39–49.
6https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00426-006-0072-4
































![Cyber AI Analyst Incident Log showing the offending device making over 1,000 connections to the suspicious hostname “zohoservice[.]net” over port 8383, within a specific period.](https://assets-global.website-files.com/626ff4d25aca2edf4325ff97/662971c1cf09890fd46729a1_Screenshot%202024-04-24%20at%201.55.10%20PM.png)